Valencia Fruits Report on Global Banana Trading
2024-07-19

The volume of bananas traded showed modest growth during the first half of 2023, indicating the potential for a significant recovery after the previous year's decline. With global exports increasing by around 0.3% compared to 2022 and the industry's leading players adapting to the changing market conditions, there is a sense of optimism for the future of the banana trade. The first half's evolution revealed disparate trends among the main banana-producing and exporting countries. While some registered increases in their shipments, others faced significant challenges that have limited their growth capacities, such as unfavourable weather conditions, high costs of fertilizers and phytosanitary products, and the spread of devastating diseases such as Fusarium wilt (TR4). This underscores the need for support and solutions to ensure the industry's sustainability.
Demand for bananas remained strong in significant import markets, particularly the European Union and the United States, driven mainly by their relative affordability compared to other fruits. This strong demand contributed to high prices, especially in these critical markets, and consequently, the sector's profitability improved in the second half of the year. The world's leading exporting regions, Latin America and the Caribbean, increased their banana shipments by 1.3% to reach 14.7 million tonnes – 200,000 more than in 2022. Ecuador, the leading banana exporter, recorded a 7% growth in its shipments between January and August 2023, raising the country's total exports to approximately 6.2 million tons. The government's increase in production by almost 10% during the first half of 2023, combined with lower sea freight rates, has significantly reduced the costs of importing bananas from Ecuador to the EU, providing a positive outlook for future growth.
Shipments from Guatemala, the LAC region's second-largest exporter in 2022 and the top exporter to the United States recorded nearly 10% growth in the first eight months of 2023, pointing to total export of 2.4 million tons in 2023. Favourable production conditions and expanding investments allowed for ample availability of low-cost bananas in Guatemala. With an average value of $380 per tonne, Guatemalan bananas remain among the cheapest on world markets.
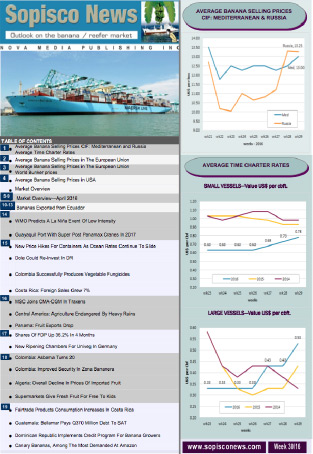
Meanwhile, exports from Colombia, the third-largest supplier in the LAC region in 2022, were affected by heavy rains in the first half of the year, which hurt both the quantity and quality of production. Preliminary data from Colombia's National Customs Office shows a year-on-year drop of nearly 30% between January and August 2023 and a 12% increase in the average export unit value. Thus, Colombia's banana exports were reduced to just under 2 million tons in 2023, a decrease of 12% compared to 2022. In addition to the adverse weather, the industry faced high costs to implement TR4 disease mitigation strategies.
Costa Rica, another major exporter and third-largest supplier to the EU, also suffered from production shortages in the first half of 2023 due to unfavourable weather conditions and insufficient fertilizer application in 2022. Data from the National Institute of Statistics of Costa Rica registered a year-on-year drop of 8.5% in the amount exported until June 2023. However, demand in the European Union and the United States, the main markets for Costa Rican bananas, remained firm, increasing the average unit value of exports by 7.8%. Asia's exports contracted by around 4% in 2023 to about 3.7 million tonnes. The region's top exporter remains the Philippines, which supplies about 60% of Asian banana shipments. However, the spread of TR4 in the country severely affected its production. Meanwhile, demand from China and some emerging importers in the Middle East helped to boost further investments in banana plantations in Vietnam and India, two rising exporters in the region. Thus, India's banana exports grew to about 450,000 tons in 2023, an increase of approximately 25% compared to 2022, and Vietnam's reached about 420,000 tons, 3% more than in 2022.
Based on the evolution of the first half, Africa's exports registered an estimated expansion of 2% in quantitative terms in 2023, reaching about 670,000 tonnes. Trade data from January to July 2023 indicated a growth in world banana imports of 1%, reaching approximately 18.7 million tonnes. While demand was firm in most markets, import growth has been constrained by reduced availability of supplies from primary producers, especially Costa Rica, Colombia, and the Philippines. This shortage mainly affected imports from the European Union, Japan, the United Kingdom, and China, accounting for almost 50% of the world.
Net banana imports from the EU, the world's largest importer, stagnated in the first seven months of 2023, pointing to a total import of 5 million tonnes for that year, 10% below pre-pandemic levels. Despite this, demand for bananas in the EU has increased, pushing import prices in key destinations such as the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, Italy, and France, with 10-15% increases.
Net imports in the United States grew by 1.5% during the first eight months of the year, reaching an annual total of approximately 4.1 million tonnes. Guatemala's imports increased by 2% – from which the United States obtains about 40% of total purchases – while Costa Rica and Ecuador grew by 10% and 7%, respectively. The sharp increase in organic banana shipments from Ecuador is worth noting, with a year-on-year increase of 21% between January and August 2023.
China's imports declined by 9% between January and August 2023, with an annual projection below 1.8 million tonnes, although it remains the world's third-largest importer, with a 9% share of global imports in 2023.
Available data indicate that the Russian Federation's net imports remained unchanged from the previous year, at 1.4 million tonnes in 2023, and these shipments were almost exclusively from Ecuador. Finally, imports from Japan decreased to 1 million tonnes due to lower production in the Philippines, which supplies 75-80% of bananas, and logistical difficulties from Ecuador.